Physics 1
Two sleds are attached by a rope and are being pulled by an applied force, Fa= 100 N. There is 40 N of frictional force opposing movement on each sled. Draw a free body diagram to help find:

Determine the acceleration and the value of the normal force. Draw a free body diagram.
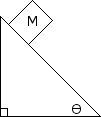
M = 10kg, = 30 degrees
A block of mass M = 5kg is placed on an incline of = 30 degrees. There is a frictional force of 15 N opposing the movement of the block. Determine the acceleration of the block. Draw a free body diagram to help find the answer.

A block of mass M = 5kg is placed on an incline of = 30 degrees. There is a frictional force opposing the movement of the block with a coefficient of friction, = 0.2. Determine the acceleration of the block. Draw a free body diagram to help find the answer.

Determine the acceleration of the system if M = 10 kg and m = 30 kg and = 30 degrees. Determine the tension in the rope as well.
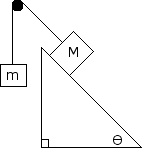
Determine the acceleration of the system if M = 5 kg and m = 10 kg and = 30 degrees. There is also a coefficient of friction, = 0.2. Use a free body diagram to determine the tension in the rope and the acceleration of the system.

The large block M is 20 kg, and the smaller block, m, is 1 kg. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.2. Determine the acceleration of the system and the tension in the cords. The angle of the inclined plane is 60 degrees to the horizontal. Also draw a free body diagram for both blocks.

Block M = 5 kg and block m = 6 kg. The coefficient of friction is 0.5. Determine the acceleration of the system and the tension in the cord. The angle of the inclined plane is 20 degrees to the horizontal. Draw a free body diagram for the 5 kg block to help find the answer.

Block M = 5 kg and block m = 3 kg. The coefficient of static friction is 0.2. Determine the acceleration of the system and the tension in the cord. The angle of the inclined plane is 30 degrees to the horizontal. Draw a free body diagram for the 5 kg block to help find the answer.

Determine the acceleration of the system if m = 5 kg and m = 10 kg and the pulley has no mass. Determine the tension in the rope as well.
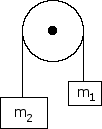
Determine the acceleration of the system if m = 3 kg and m = 8 kg and the pulley has no mass. Determine the tension in the rope as well.

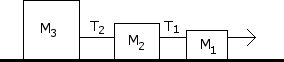
Determine the acceleration of the system if m = 5 kg and m = 10 kg and m. Determine the tensions T, T , and T .
A 3 kg box is pushed on a surface with a force of F = 15 N. The coefficient of static friction, is 0.3, and the coefficient of kinetic friction, is 0.1.
A. Does the box move?
B. If it does move, calculate the acceleration of the box.
A M = 5 kg box rests on a table and is connected to a second box of mass M = 10 kg via a rope that hangs over a frictionless pulley as shown. The coefficient of friction, is 0.2, Use free body diagrams to answer the following:
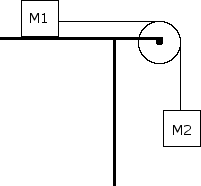
B. What is the tension in the rope?
A M = 6 kg box rests on a table and is connected to a second box of mass M = 5 kg via a rope that hangs over a frictionless pulley as shown. The coefficient of friction, is 0.15, Use free body diagrams to answer the following:

B. What is the tension in the rope?
A M = 8 kg box rests on a table and is connected to a second box of mass M = 4 kg via a rope that hangs over a pulley as shown. The coefficient of static friction, is 0.2, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.1. Use a free body diagrams to answer the following.

B. If the box does cause the system to move, what is the acceleration of the system, and the tension in the rope?
The large block m is 10 kg, and the smaller block m is 5 kg. The applied force, F is 100 N. The large block m experiences a 40 N frictional force opposing the applied force, and the smaller block m experiences a 20 N frictional force. Find the action-reaction force between the boxes. (This question requires Newton's Third Law.)
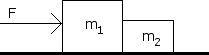
The large block m is 10 kg, and the smaller block m is 1 kg. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.1. Determine the acceleration of the system and the contact force between the blocks. The applied force, F is 30 N. Also draw a free body diagram for both blocks.
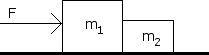
The large block m is 6 kg, and the smaller block m is 12 kg. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.2. Determine the acceleration of the system and the Tension T . The applied force, F is 36 N. Also draw a free body diagram for both blocks.

A ball of mass M is thrown vertically upward with an initial speed of v0. It experiences a force of air resistance given by F=−kv, where k is a positive constant. The positive direction for all vector quantities is upward. Express all algebraic answers in terms of M, k, v0, and fundamental constants.
Does the magnitude of the acceleration of the ball increase, decrease, or remain the same as the ball moves upward?
Write, but do NOT solve, a differential equation for the instantaneous speed vof the ball in terms of time tas the ball moves upward.
Determine the terminal speed of the ball as it moves downward.
Does it take longer for the ball to rise to its maximum height or to fall from its maximal height back to the height from which it was thrown? Justify your answer.
Sketch a graph of velocity versus time for the upward and downward parts of the ball’s flight, where is the time at which the ball returns to the height from which it was thrown.