Friction Physics
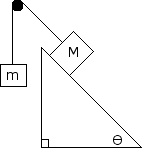
Determine the acceleration of the system if M = 5 kg and m = 10 kg and = 30 degrees. There is also a coefficient of friction, = 0.2. Use a free body diagram to determine the tension in the rope and the acceleration of the system.
Related Problems
An Object with mass m and initial velocity v is brought to rest by a constant force F acting for a time t and through a distance d. Possible expressions for the magnitude of the force F are: i. ii. iii.
ii only
iii only
i and ii only
ii and iii only
i, ii, and iii
A toy car of mass 6 kg moving in a straight path, experiences a net force given by the function F = -3t. At time t=0, the car has a velocity of 4 m/s in the positive direction and is located +8 m from the origin. The car will come instantaneously to rest at time t equal to
2/3 s
sqrt( 4/3 ) s
sqrt( 8/3 ) s
sqrt( 8) s
4 s
The large block M is 20 kg, and the smaller block, m, is 1 kg. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.2. Determine the acceleration of the system and the tension in the cords. The angle of the inclined plane is 60 degrees to the horizontal. Also draw a free body diagram for both blocks.

Block M = 5 kg and block m = 6 kg. The coefficient of friction is 0.5. Determine the acceleration of the system and the tension in the cord. The angle of the inclined plane is 20 degrees to the horizontal. Draw a free body diagram for the 5 kg block to help find the answer.
