Physics: Pulley Friction
A M = 5 kg box rests on a table and is connected to a second box of mass M = 10 kg via a rope that hangs over a frictionless pulley as shown. The coefficient of friction, is 0.2, Use free body diagrams to answer the following:
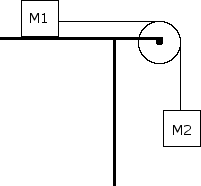
B. What is the tension in the rope?
Related Problems
An Object with mass m and initial velocity v is brought to rest by a constant force F acting for a time t and through a distance d. Possible expressions for the magnitude of the force F are: i. ii. iii.
ii only
iii only
i and ii only
ii and iii only
i, ii, and iii
A toy car of mass 6 kg moving in a straight path, experiences a net force given by the function F = -3t. At time t=0, the car has a velocity of 4 m/s in the positive direction and is located +8 m from the origin. The car will come instantaneously to rest at time t equal to
2/3 s
sqrt( 4/3 ) s
sqrt( 8/3 ) s
sqrt( 8) s
4 s
A M = 6 kg box rests on a table and is connected to a second box of mass M = 5 kg via a rope that hangs over a frictionless pulley as shown. The coefficient of friction, is 0.15, Use free body diagrams to answer the following:

B. What is the tension in the rope?
A M = 8 kg box rests on a table and is connected to a second box of mass M = 4 kg via a rope that hangs over a pulley as shown. The coefficient of static friction, is 0.2, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.1. Use a free body diagrams to answer the following.

B. If the box does cause the system to move, what is the acceleration of the system, and the tension in the rope?