Free Body Diagram Example
A block of mass M = 5kg is placed on an incline of = 30 degrees. There is a frictional force of 15 N opposing the movement of the block. Determine the acceleration of the block. Draw a free body diagram to help find the answer.
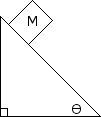
To determine the acceleration of the block on the incline, first draw a free body diagram showing all the forces acting on it: gravity pulling downward, a normal force perpendicular to the incline, and a frictional force opposing the motion along the surface. Break down the gravitational force into components parallel and perpendicular to the incline; then, subtract the frictional force from the parallel component. Use Newton's second law to calculate the net force and divide by the mass to find the acceleration.
Related Problems
An Object with mass m and initial velocity v is brought to rest by a constant force F acting for a time t and through a distance d. Possible expressions for the magnitude of the force F are: i. ii. iii.
ii only
iii only
i and ii only
ii and iii only
i, ii, and iii
A toy car of mass 6 kg moving in a straight path, experiences a net force given by the function F = -3t. At time t=0, the car has a velocity of 4 m/s in the positive direction and is located +8 m from the origin. The car will come instantaneously to rest at time t equal to
2/3 s
sqrt( 4/3 ) s
sqrt( 8/3 ) s
sqrt( 8) s
4 s
A block of mass M = 5kg is placed on an incline of = 30 degrees. There is a frictional force opposing the movement of the block with a coefficient of friction, = 0.2. Determine the acceleration of the block. Draw a free body diagram to help find the answer.

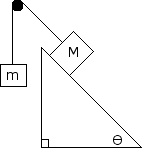
Determine the acceleration of the system if M = 10 kg and m = 30 kg and = 30 degrees. Determine the tension in the rope as well.