Physics 1: Free Body Diagrams
As shown in the figure, two blocks with masses m and M (M>m) are pushed by a force F in both Case I and Case II. The surface is horizontal and frictionless. Let R1 be the force that m exerts on M in Case I and RII be the force that m exerts on M in Case II. Which of the following statements is true?

Two boxes with masses 17 kg and 15 kg are connected by a light string that passes over a frictionless pulley of negligible mass as shown in the figure below. The surfaces of the planes are frictionless. The blocks are released from rest. T1 and T2 are the tensions in the strings. Which of the following statements is correct?

A toy car of mass 6 kg moving in a straight path, experiences a net force given by the function F = -3t. At time t=0, the car has a velocity of 4 m/s in the positive direction and is located +8 m from the origin. The car will come instantaneously to rest at time t equal to
2/3 s
sqrt( 4/3 ) s
sqrt( 8/3 ) s
sqrt( 8) s
4 s
In the situation above, what is the ratio of the masses?
0.67
1.0
1.4
1.5
1.6
Hercules and Carlos horizontally push in the same direction on a 1200 kg crate. Hercules pushes with a force of 500 N and Carlos pushes with a force of 300 N. If a frictional force provides 200 N of resistance, what is the acceleration of the crate?
1.3 m/s2
1.0 m/s2
0.87 m/s2
0.75 m/s2
0.5 m/s2
Two sleds are attached by a rope and are being pulled by an applied force, Fa= 100 N. There is 40 N of frictional force opposing movement on each sled. Draw a free body diagram to help find:

Determine the acceleration of the system if M = 5 kg and m = 10 kg and = 30 degrees. There is also a coefficient of friction, = 0.2. Use a free body diagram to determine the tension in the rope and the acceleration of the system.
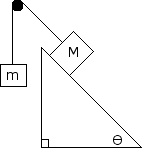
The large block M is 20 kg, and the smaller block, m, is 1 kg. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.2. Determine the acceleration of the system and the tension in the cords. The angle of the inclined plane is 60 degrees to the horizontal. Also draw a free body diagram for both blocks.

Block M = 5 kg and block m = 6 kg. The coefficient of friction is 0.5. Determine the acceleration of the system and the tension in the cord. The angle of the inclined plane is 20 degrees to the horizontal. Draw a free body diagram for the 5 kg block to help find the answer.

Determine the acceleration of the system if m = 3 kg and m = 8 kg and the pulley has no mass. Determine the tension in the rope as well.
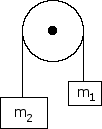
Determine the acceleration of the system if m = 5 kg and m = 10 kg and m. Determine the tensions T, T , and T .
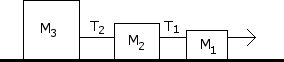
A 3 kg box is pushed on a surface with a force of F = 15 N. The coefficient of static friction, is 0.3, and the coefficient of kinetic friction, is 0.1.
A. Does the box move?
B. If it does move, calculate the acceleration of the box.
A M = 5 kg box rests on a table and is connected to a second box of mass M = 10 kg via a rope that hangs over a frictionless pulley as shown. The coefficient of friction, is 0.2, Use free body diagrams to answer the following:
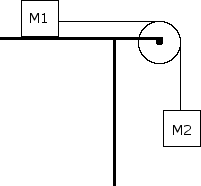
B. What is the tension in the rope?
The large block m is 10 kg, and the smaller block m is 1 kg. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.1. Determine the acceleration of the system and the contact force between the blocks. The applied force, F is 30 N. Also draw a free body diagram for both blocks.
A box is being pulled with force Fa= 40 N at an angle θ= 30 degrees. There is a frictional force opposing the sliding of the box with force Ff= 10 N. Draw a free body diagram to help answer the following questions. (use gravity at 10m/s2 to simplify the numbers)
