Physics 1: Impulse and Momentum
A 2kg car is traveling east at 3 m/s and a 4kg car is traveling west at 6 m/s. Assume the cars collide and stick together. Find the direction and velocity of the cars after they collide.
A 2kg car is traveling east at 3 m/s and a 4kg car is traveling west at 6 m/s. Now assume the cars bounce off each other in a perfectly elastic collision. The final velocity of the 2kg car is -4 m/s. Find the direction and velocity of the other car after the collision.
A champagne bottle of mass 90 g has a 2 g cork in it. The pressure built up in the bottle causes the cork to shoot out, as shown below. If after the explosion, the bottle is moving directly to the left at 4 m/s, what is the velocity of the cork?
The red ball (4 kg) hits the blue ball (5 kg) moving at 2 m/s, and the balls move as shown in the figure below. = 30 degrees. After the impact, the red ball is measured moving at 1.8 m/s. What is the velocity of the blue ball, and at what angle relative to the horizontal is the ball moving after the impact?

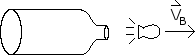
The mass shown below is blown apart into three pieces. Find the direction and velocity of the pink piece.
A crash test car of mass 1,000 kg moving at a constant speed of 12 m/s collides completely inelastically with an object of mass M at time t = 0. The ojbect was initally at rest. The speed v in m/s of the car object system after the collision is given as a function of time t in seconds by the expression
A. Calculate the mass M of the object
B. Assuming an initial position of x = 0, determine an expression for the position of the car object system after the collision as a function of time t.
C. Determine an expression for the resisting force on the car object system after the collision as a function of time t.
D. Determine the impulse delivered to the car object system from t = 0 to t = 2.0 s.
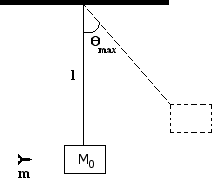
In a laboratory experiment, you wish to determine the initial speed of a dart just after it leaves a dart gun. The dart of mass is fired with the gun very close to a wooden block of mass which hangs from a cord of length and negligible mass as shown below. Assume the size of the block is negligible compared to and the dart is moving horizontally when it hits the left side of the block at its center and becomes embedded in it. The block swings up to a maximum angle from the vertical. Express your answer to the following in terms of , , , , and .
C. The dart is now shot into a block of wood that is fixed in place. The block exerts a force F on the dart that is proportional to the dart's velocity v and in the opposite direction, that is F = -bv, where b is a constant. Derive an expression for the distance L that the dart penetrates into the block in terms of m, , and b.