Orbital Velocity
An explorer plans a mission to place a satellite into a circular orbit around the planet Jupiter, which has a mass of M1= 1.90 x 1027kg and radius R1= 7.14 x 107m. A. If the radius of the planned orbit is R, use Newton’s laws to show each of the following.
The orbital speed of the planned satellite is give by v=
The period of the orbit is given by T=
B. The explorer wants the satellite’s orbit to be synchronized with Jupiter’s rotation. This requires an equatorial orbit whose period equals Jupiter’s rotation period of 9 hr 51 min = 3.55 x 105s. Determine the required orbital radius in meters. C. Suppose that the injection of the satellite into orbit is less than perfect. For an injection velocity that differs form the desired value in each of the following ways, sketch the resulting orbit on the figure. ( J is the center of Jupiter, the dashed circle is the desired orbit, and Pis the injection point.) Also, describe the resulting orbit qualitatively but specifically
When the satellite is at the desired altitude over the equator, its velocity vector has the correct direction, but the speed is slightly faster than the correct speed for a circular orbit of that radius.
When the satellite is at the desired altitude over the equation, its velocity vector has the correct direction but the speed is slightly slower than the correct speed for a circular orbit of that radius.

SOLUTION MISSING: Unfortunately the author of this youtube video removed their content. You may be able to find a similar problem by checking the other problems in this subject. If you want to contribute, leave a comment with the link to your solution.
Related Problems
A massless string is wrapped around a disk of rotational inertia I = . The disk falls and spins as it falls, unraveling the rope. Determine the tension in the string and the acceleration of the disk.
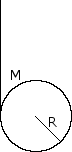
A solid brass sphere of mass m and radius r << R rolls along a track when released from rest along the straight section. The circular loop has a radius R.
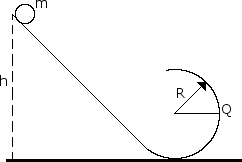
B. Assume the sphere is released at height h = 6.0 R, what are the magnitude and direction of the horizontal force competent acting on the sphere at point Q?
A light string that is attached to a large block of mass 4m passes over a pulley with negligible rotational inertia and is wrapped around a vertical pole of radius r, as shown below. The system is released from rest, and as the block descends the string unwinds and the vertical pole with its attached apparatus rotates. The apparatus consists of a horizontal rod of length 2L, with a small block of mass m attached at each end. The rotational inertia of the pole and the rod are negligible.

D. When the large block has descended a distance D, how does the instantaneous total kinetic energy of the three blocks compare to that in part (C), Greater, Equal, or Less?
A uniform disk is mounted to an axle and is free to rotate without friction. A thin uniform rod is rigidly attached to the disk so that it will rotate with the disk. A block is attached to the end of the rod. Properties of the disk, rod, and block are as follows.

C. Determine the linear speed of the mass at the end of the rod for the instant the rod is in the horizontal position.