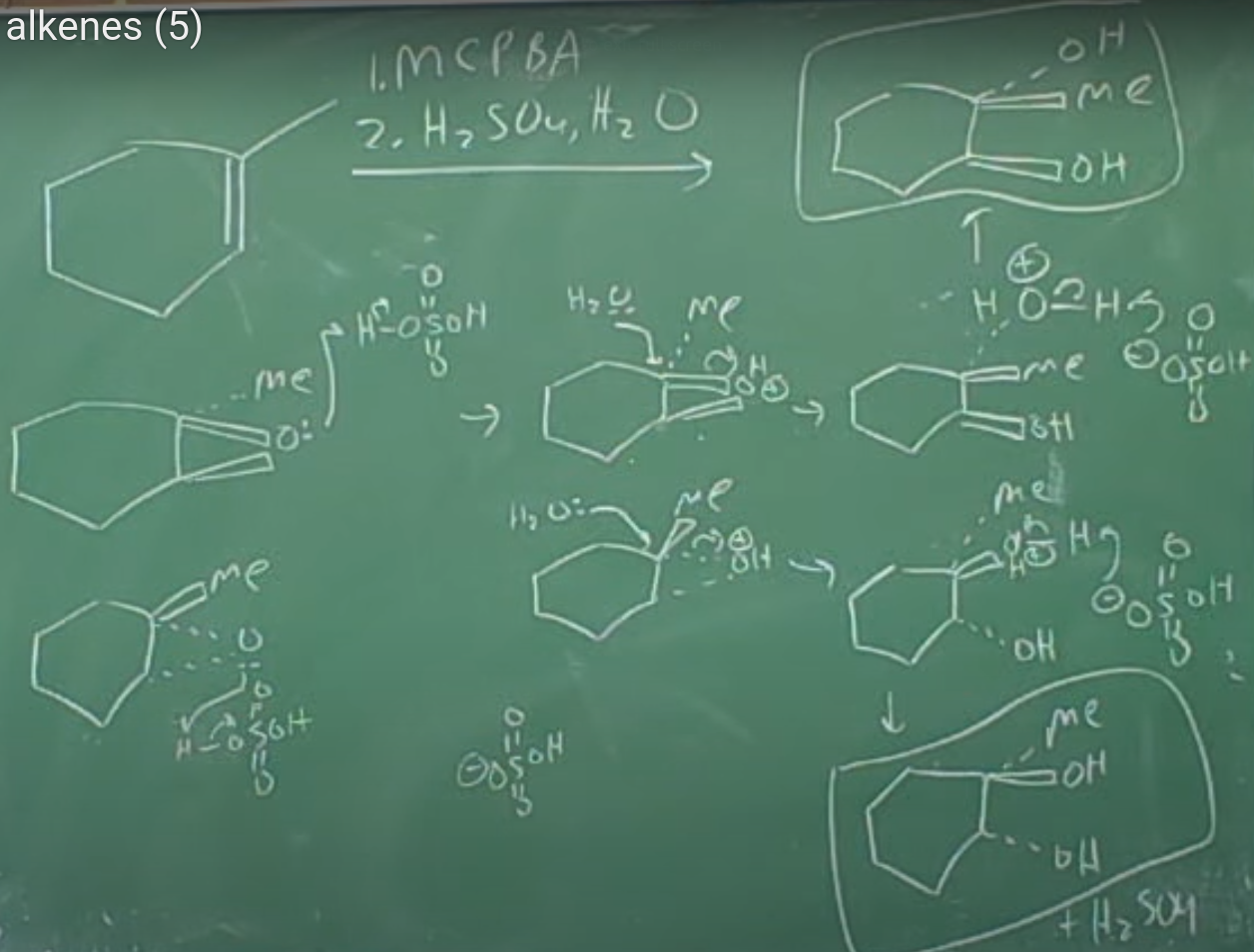
MCPBA Alkene Reaction
Provide the major products for the reaction. Show the sterochemistry of the products. MCPBA is meta-chloroperoxybenzoic acid
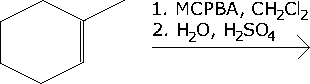
Oxidation of Alkenes: Epoxidation and Hydroxylation The word oxidation has a slightly different meaning in organic chemistry than what you might have previously learned. In general chemistry, an oxidation is defined as the loss of one or more electrons by an atom. In organic chemistry, however, an oxidation is a reaction that results in a loss of electron density for carbon, caused either by bond formation between carbon and a more electronegative atom—usually oxygen, nitrogen, or a halogen—or by bond-breaking between carbon and a less electronegative atom—usually hydrogen. Note that an oxidation often adds oxygen, while a reduction often adds hydrogen.
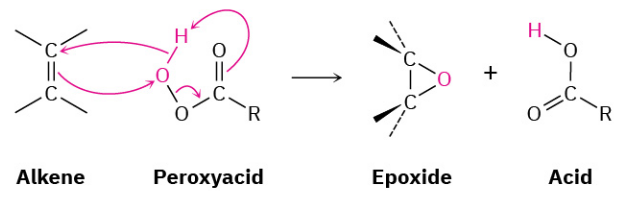
Peroxyacids transfer an oxygen atom to the alkene with syn stereochemistry—both C−O bonds form on the same face of the double bond—through a one-step mechanism without intermediates. The oxygen atom farthest from the carbonyl group is the one transferred.